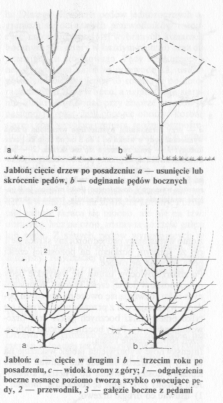
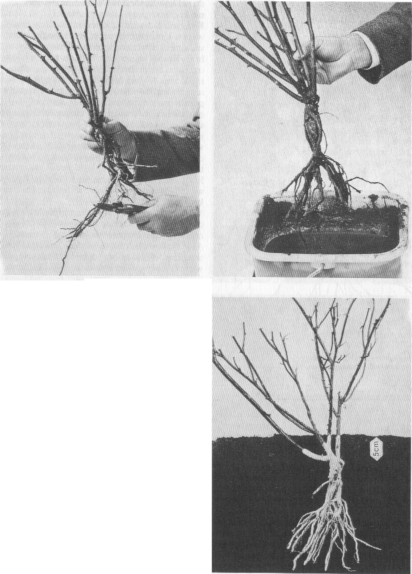
Sposób cięcia w drugim roku po posadzeniu zależy od długości i grubości pędu jednorocznego. Pęd taki może mieć od 30 do 200 cm długości. Pęd długości 200 cm dowodzi, że wysadzono zdrową i silną sadzonkę oraz że pielęgnacja i nawożenie roślin były właściwe. Bardzo słaby wzrost świadczy o tym, że podczas sadzenia i pielęgnacji w pierwszym roku popełniono błędy. Należy wtedy zasięgnąć informacji u fachowca. Jeżeli jednak nie uda się ustalić powodu słabego wzrostu, lepiej posadzić nowe sadzonki.
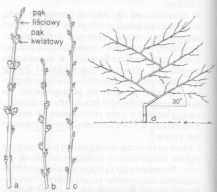
 Niezależnie od sposobu cięcia i prowadzenia krzewu pęd jednoroczny trzeba mocno skrócić, co sprzyja rozwojowi silnego i prostego pnia. Sadzonkę tuż po posadzeniu skraca się nad trzecim oczkiem. Jeśli w pierwszym roku z tych oczek wyrosną pędy, to najsilniejszy z nich przywiązuje się pionowo, gdy osiągnie długość 10—20 cm, a pozostałe się usuwa. Młody pęd przywiązuje się do podpory w odstępach co 25 cm. Wczesną wiosną następnego roku skraca się ten pęd nad 6. oczkiem, około 30 cm od powierzchni gleby, zostawiając czop nad oczkiem długości około 2 cm. Aby uniknąć „płaczu” skracanego pędu, zabieg ten trzeba wykonać podczas pogody bezmroźnej. Pozostawienie 2-cen-tymetrowego czopa chroni rdzeń młodego pędu przed wysuszeniem. Po każdym cięciu zimowym krzewów konieczne jest cięcie letnie, także krzewów posadzonych na wiosnę. Rozpoczyna się wtedy formowanie sznura pionowego przez tzw. cięcie na czop, co jest szczególnie polecane dla odmian słabo rosnących. Na młodych pędach wyrastających z dolnych oczek rozwija się od 1 do 3 kwiatostanów. W następnym roku pierwsze pięć bocznych pędów skraca się na dwa oczka, a szósty na sześć oczek. Tak postępuje się co roku, aż krzew osiągnie pożądaną wysokość.
Niezależnie od sposobu cięcia i prowadzenia krzewu pęd jednoroczny trzeba mocno skrócić, co sprzyja rozwojowi silnego i prostego pnia. Sadzonkę tuż po posadzeniu skraca się nad trzecim oczkiem. Jeśli w pierwszym roku z tych oczek wyrosną pędy, to najsilniejszy z nich przywiązuje się pionowo, gdy osiągnie długość 10—20 cm, a pozostałe się usuwa. Młody pęd przywiązuje się do podpory w odstępach co 25 cm. Wczesną wiosną następnego roku skraca się ten pęd nad 6. oczkiem, około 30 cm od powierzchni gleby, zostawiając czop nad oczkiem długości około 2 cm. Aby uniknąć „płaczu” skracanego pędu, zabieg ten trzeba wykonać podczas pogody bezmroźnej. Pozostawienie 2-cen-tymetrowego czopa chroni rdzeń młodego pędu przed wysuszeniem. Po każdym cięciu zimowym krzewów konieczne jest cięcie letnie, także krzewów posadzonych na wiosnę. Rozpoczyna się wtedy formowanie sznura pionowego przez tzw. cięcie na czop, co jest szczególnie polecane dla odmian słabo rosnących. Na młodych pędach wyrastających z dolnych oczek rozwija się od 1 do 3 kwiatostanów. W następnym roku pierwsze pięć bocznych pędów skraca się na dwa oczka, a szósty na sześć oczek. Tak postępuje się co roku, aż krzew osiągnie pożądaną wysokość.
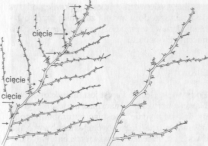
Cięcie letnie polega na uszczykiwaniu pędów owoconośnych nad szóstym liściem najwyżej położonego kwiatostanu, gdy jagody osiągną średnicę 2 mm. Wyrastające z kątów liści pasierby (młode pędy) uszczykuje się nad pierwszym liściem. Z tej części wyrasta nowy pęd, który także uszczykuje się bardzo krótko, co zagwarantuje lepsze nasłonecznienie gron. Pęd główny natomiast skraca się nad dwunastym, a pasierby z niego wyrastające nad pierwszym liściem. Aby na przewodniku (pęd główny) zawsze było pod dostatkiem pędów bocznych, pęd ten należy wczesną wiosną skrócić nad szóstym oczkiem.
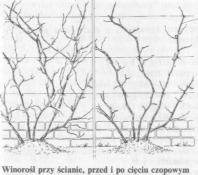
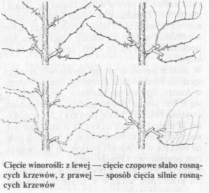
Odmiany silnie rosnące wymagają innego cięcia, tzw. cięcia długiego. Krzewy prowadzone w formie szpalerowej w krótkim czasie zajmują większą powierzchnię ściany. Przy tym sposobie cięcia z wyżej położonych oczek wybija od 3 do 5 kwiatostanów. Krzewy prowadzone w formie szpaleru z zastosowaniem cięcia długiego również wymagają wyprowadzenia przewodnika, z którego wyrastają silne pędy boczne. Zanim u-tworzy się pierwsze piętro wyrastają pierwsze grona na pędzie głównym. Zasada cięcia długiego jest następująca: wczesną wiosną skraca się boczne pędy na dwa oczka (czop). Z oczek tych wyrastają dwa pędy. Dolny skraca się znowu na dwa oczka, a górny nad 6—8 oczkiem i przywiązuje do szpaleru na ścianie (Trenkle 1941). W razie nadmiaru pędów w lecie usuwa się cienkie i zbyteczne. Zasadniczym celem jest uzyskanie niezbyt licznych za to silnych pędów oraz dobre zapełnienie miejsca na ścianie. Cięcie letnie jest podobne do cięcia na czop, czyli cięcia krótkiego.
W małym ogrodzie można spróbować nowego sposobu formowania krzewów, opracowanego w Austrii. Sposób ten nazwano „wysoką uprawą”. Nie jest to równoznaczne z określeniem „wysoka roślina”, której pień ma 1,5 m wysokości. W metodzie austriackiej na drutach lub listwach (szpaler) przymocowane są pędy lub gałęzie rosnące w położeniu poziomym lub zwisającym (sposób wg Lenz-Moser).
Winorośl była kiedyś podarunkiem Rzymian. Na przestrzeni wieków w środkowej Europie uprawa winorośli bardzo się rozpowszechniła, często jako monokultura. Taka jednostronna uprawa ma też swoje ujemne strony, które można wyeliminować w małym ogrodzie. Warto posadzić winorośl i przestrzegać biodynamicznych metod jej uprawy.
Pielęgnacja winorośli w ciągu roku
Początek wegetacji preparat krowieńca z dodatkiem naparu ze skrzypu
Kiedy pędy osiągną długość:
20 cm Bio-S- 60 g/10 l wody
40 cm preparat krzemionki
50 cm Bio-S – 60—80 g/10 l wody
60 cm Bio-S- 60—80 g/10 l wody
Początek kwitnienia Bio-S” 60 g/10 l wody
14 dni później Bio-S- 60 g/10 l wody
Kiedy jagody mają średnicę 2 mm preparat krzemionki
W odstępach 10 —12 dni Bio-S- 60—80 g/10 l wody
Koniec sierpnia — połowa września dwukrotnie preparat krzemionki w godzinach popołudniowych
Po opadnięciu liści nawożenie rozłożonym kompostem, w dawce od 0,5 do 2 wiader pod krzew